- Chapter 11: Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
- 11.1: What is Physics?
- 11.2: Rolling as Translation and Rotation
Combined (2)
- 11.3: The Kinetic Energy of Rolling
- 11.4: The Forces of Rolling (12)
- 11.5: The Yo-Yo (2)
- 11.6: Torque Revisited (7)
- 11.7: Angular Momentum (6)
- 11.8: Newton's Second Law in Angular Form
(3)
- 11.9: The Angular Momentum of a System of
Particles
- 11.10: The Angular Momentum of a Rigid Body
Rotating About a Fixed Axis (5)
- 11.11: Conservation of Angular Momentum
(22)
- 11.12: Precession of a Gyroscope (1)
- 11: Additional Problems (26)
- 11: Guided Online Tutorials (4)
- Testbank (54)
- Symbolic Notation (6)
- Simulations
- Conceptual Questions (7)
- Chapter 12: Equilibrium and Elasticity
- 12.1: What is Physics?
- 12.2: Equilibrium
- 12.3: The Requirements of Equilibrium
- 12.4: The Center of Gravity
- 12.5: Some Examples of Static Equilibrium
(28)
- 12.6: Indeterminate Structures
- 12.7: Elasticity (5)
- 12: Additional Problems (20)
- 12: Guided Online Tutorials (4)
- Testbank (53)
- Symbolic Notation (6)
- Simulations (2)
- Conceptual Questions (3)
- Chapter 13: Gravitation
- 13.1: What is Physics?
- 13.2: Newton's Law of Gravitation (4)
- 13.3: Gravitation and the Principle of
Superposition (6)
- 13.4: Gravitation Near Earth's Surface
(5)
- 13.5: Gravitation Inside Earth (3)
- 13.6: Gravitation Potential Energy
(10)
- 13.7: Planets and Satellites: Kepler's Laws
(12)
- 13.8: Satellites: Orbits and Energy
(4)
- 13.9: Einstein and Gravitation (1)
- 13: Additional Problems (18)
- 13: Guided Online Tutorials (3)
- Testbank (56)
- Symbolic Notation (5)
- Simulations (1)
- Conceptual Questions (3)
- Chapter 14: Fluids
- 14.1: What is Physics?
- 14.2: What is a Fluid?
- 14.3: Density and Pressure (6)
- 14.4: Fluids at Rest (8)
- 14.5: Measuring Pressure (2)
- 14.6: Pascal's Principle
- 14.7: Archimedes' Principle (11)
- 14.8: Ideal Fluids in Motion
- 14.9: The Equation of Continuity (4)
- 14.10: Bernoulli's Equation (5)
- 14: Additional Problems (7)
- 14: Guided Online Tutorials (3)
- Testbank (85)
- Symbolic Notation (5)
- Simulations
- Conceptual Questions (2)
- Chapter 15: Oscillations
- 15.1: What is Physics?
- 15.2: Simple Harmonic Motion
- 15.3: The Force Law for Simple Harmonic
Motion (17)
- 15.4: Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion
(7)
- 15.5: An Angular Simple Harmonic Oscillator
(2)
- 15.6: Pendulums (7)
- 15.7: Simple Harmonic Motion and Uniform
Circular Motion
- 15.8: Damped Simple Harmonic Motion
(3)
- 15.9: Forced Oscillations and Resonance
(1)
- 15: Additional Problems (24)
- 15: Guided Online Tutorials (7)
- Testbank (62)
- Symbolic Notation (5)
- Simulations (1)
- Conceptual Questions (4)
- Chapter 16: Waves - I
- 16.1: What is Physics?
- 16.2: Types of Waves
- 16.3: Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
- 16.4: Wavelength and Frequency
- 16.5: The Speed of a Traveling Wave
(7)
- 16.6: Wave Speed on a Stretched String
(10)
- 16.7: Energy and Power of a Wave Traveling
Along a String (1)
- 16.8: The Wave Equation (2)
- 16.9: The Principle of Superposition for
Waves
- 16.10: Interference of Waves (2)
- 16.11: Phasors (2)
- 16.12: Standing Waves
- 16.13: Standing Waves and Resonance
(16)
- 16: Additional Problems (19)
- 16: Guided Online Tutorials (1)
- Testbank (71)
- Symbolic Notation (5)
- Simulations (6)
- Conceptual Questions (1)
- Chapter 17: Waves - II
- 17.1: What is Physics?
- 17.2: Sound Waves
- 17.3: The Speed of Sound (5)
- 17.4: Traveling Sound Waves (3)
- 17.5: Interference (4)
- 17.6: Intensity and Sound Level (9)
- 17.7: Sources of Musical Sound (8)
- 17.8: Beats (4)
- 17.9: The Doppler Effect (8)
- 17.10: Supersonic Speeds, Shock Waves
(1)
- 17: Additional Problems (16)
- 17: Guided Online Tutorials (3)
- Testbank (61)
- Symbolic Notation (5)
- Simulations (4)
- Conceptual Questions (1)
- Chapter 18: Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of
Thermodynamics
- 18.1: What is Physics?
- 18.2: Temperature
- 18.3: The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
- 18.4: Measuring Temperature (1)
- 18.5: The Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
(2)
- 18.6: Thermal Expansion (9)
- 18.7: Temperature and Heat
- 18.8: The Absorption of Heat by Solids and
Liquids (13)
- 18.9: A Closer Look at Heat and Work
- 18.10: The First Law of Thermodynamics
- 18.11: Some Special Cases of the First Law
of Thermodynamics (4)
- 18.12: Heat Transfer Mechanisms (8)
- 18: Additional Problems (8)
- 18: Guided Online Tutorials (6)
- Testbank (82)
- Symbolic Notation (5)
- Simulations (2)
- Conceptual Questions (1)
- Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases
- 19.1: What is Physics?
- 19.2: Avogadro's Number (2)
- 19.3: Ideal Gases (9)
- 19.4: Pressure, Temperature, and RMS Speed
(6)
- 19.5: Translational Kinetic Energy (2)
- 19.6: Mean Free Path (3)
- 19.7: The Distribution of Molecular Speeds
(3)
- 19.8: The Molar Specific Heats of an Ideal
Gas (3)
- 19.9: Degrees of Freedom and Molar Specific
Heats (2)
- 19.10: A Hint of Quantum Theory
- 19.11: The Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal
Gas (4)
- 19: Additional Problems (9)
- 19: Guided Online Tutorials (6)
- Testbank (96)
- Symbolic Notation (5)
- Simulations
- Conceptual Questions (1)
- Chapter 20: Entropy and the Second Law of
Thermodynamics
- 20.1: What is Physics?
- 20.2: Irreversible Processes and Entropy
- 20.3: Change in Entropy (11)
- 20.4: The Second Law of Thermodynamics
- 20.5: Entropy in the Real World: Engines
(6)
- 20.6: Entropy in the Real World:
Refrigerators (6)
- 20.7: The Efficiencies of Real Engines
- 20.8: A Statistical View of Entropy
- 20: Additional Problems (9)
- 20: Guided Online Tutorials (6)
- Testbank (56)
- Symbolic Notation (5)
- Simulations
- Conceptual Questions (1)
- Chapter 21: Electric Charge
- 21.1: What is Physics?
- 21.2: Electric Charge
- 21.3: Conductors and Insulators
- 21.4: Coulomb's Law (16)
- 21.5: Charge Is Quantized (9)
- 21.6: Charge Is Conserved (1)
- 21: Additional Problems (22)
- 21: Guided Online Tutorials (6)
- Testbank (45)
- Symbolic Notation
- Simulations
- Conceptual Questions (7)
- Chapter 22: Electric Fields
- 22.1: What is Physics?
- 22.2: The Electric Field
- 22.3: Electric Field Lines (1)
- 22.4: The Electric Field Due to a Point
Charge (13)
- 22.5: The Electric Field Due to an Electric
Dipole (1)
- 22.6: The Electric Field Due to a Line of
Charge (9)
- 22.7: The Electric Field Due to a Charged
Disk (5)
- 22.8: A Point Charge in an Electric Field
(14)
- 22.9: A Dipole in an Electric Field
(5)
- 22: Additional Problems (22)
- 22: Guided Online Tutorials (6)
- Testbank (45)
- Symbolic Notation (4)
- Simulations (2)
- Conceptual Questions (6)
- Chapter 23: Gauss' Law
- 23.1: What is Physics?
- 23.2: Flux
- 23.3: Flux of an Electric Field (3)
- 23.4: Gauss' Law (10)
- 23.5: Gauss' Las and Coulomb's Law
- 23.6: A Charged Isolated Conductor (4)
- 23.7: Applying Gauss' Law: Cylindrical
Symmetry (9)
- 23.8: Applying Gauss' Law: Planar Symmetry
(8)
- 23.9: Applying Gauss' Law: Spherical
Symmetry (8)
- 23: Additional Problems (22)
- 23: Guided Online Tutorials (5)
- Testbank (38)
- Symbolic Notation (7)
- Simulations (4)
- Conceptual Questions (7)
- Chapter 24: Electric Potential
- 24.1: What is Physics?
- 24.2: Electric Potential Energy
- 24.3: Electric Potential (3)
- 24.4: Equipotential Surfaces
- 24.5: Calculating the Potential from the
Field (7)
- 24.6: Potential Due to a Point Charge
- 24.7: Potential Due to a Group of Point
Charges (6)
- 24.8: Potential Due to an Electric Dipole
(2)
- 24.9: Potential Due to a Continuous Charge
Distribution (9)
- 24.10: Calculating the Field from the
Potential (5)
- 24.11: Electric Potential Energy of a System
of Point Charges (15)
- 24.12: Potential of a Charged Isolated
Conductor (5)
- 24: Additional Problems (33)
- 24: Guided Online Tutorials (7)
- Testbank (43)
- Symbolic Notation (3)
- Simulations
- Conceptual Questions (10)
- Chapter 25: Capacitance
- 25.1: What is Physics?
- 25.2: Capacitance (2)
- 25.3: Calculating the Capacitance (5)
- 25.4: Capacitors in Parallel and in Series
(16)
- 25.5: Energy Stored in an Electric Field
(7)
- 25.6: Capacitor with a Dielectric (10)
- 25.7: Dielectrics: An Atomic View
- 25.8: Dielectrics and Gauss' Law (5)
- 25: Additional Problems (17)
- 25: Guided Online Tutorials (6)
- Testbank (55)
- Symbolic Notation (6)
- Simulations
- Conceptual Questions (9)
- Chapter 26: Current and Resistance
- 26.1: What is Physics?
- 26.2: Electric Current (3)
- 26.3: Current Density (10)
- 26.4: Resistance and Resistivity (19)
- 26.5: Ohm's Law
- 26.6: A Microscopic View of Ohm's Law
- 26.7: Power in Electric Circuits (15)
- 26.8: Semiconductors
- 26.9: Superconductors
- 26: Additional Problems (20)
- 26: Guided Online Tutorials (6)
- Testbank (50)
- Symbolic Notation
- Simulations
- Conceptual Questions (7)
- Chapter 27: Circuits
- 27.1: What is Physics?
- 27.2: "Pumping" Charges
- 27.3: Work, Energy, and Emf
- 27.4: Calculating the Current in a
Single-Loop Circuit
- 27.5: Other Single-Loop Circuits
- 27.6: Potential Difference Between Two
Points (17)
- 27.7: Multiloop Circuits (16)
- 27.8: The Ammeter and the Voltmeter
(5)
- 27.9: RC Circuits (12)
- 27: Additional Problems (29)
- 27: Guided Online Tutorials (5)
- Testbank (69)
- Symbolic Notation (5)
- Simulations (8)
- Conceptual Questions (9)
- Chapter 28: Magnetic Fields
- 28.1: What is Physics?
- 28.2: What Produces a Magnetic Field?
- 28.3: The Definition of
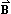 (6)
(6)
- 28.4: Crossed Fields: Discovery of an
Electron (5)
- 28.5: Crossed Fields: The Hall Effect
(2)
- 28.6: A Circulating Charged Particle
(15)
- 28.7: Cyclotrons and Synchrotrons (3)
- 28.8: Magnetic Force on a Current-Carrying
Wire (7)
- 28.9: Torque on a Current Loop (6)
- 28.10: The Magnetic Dipole Moment (10)
- 28: Additional Problems (13)
- 28: Guided Online Tutorials (6)
- Testbank (48)
- Symbolic Notation (6)
- Simulations
- Conceptual Questions (8)
- Chapter 29: Magnetic Fields Due to Currents
- 29.1: What is Physics?
- 29.2: Calculating the Magnetic Field Due to
a Current (24)
- 29.3: Force Between Two Parallel Currents
(4)
- 29.4: Ampere's Law (5)
- 29.5: Solenoids and Toroids (7)
- 29.6: A Current-Carrying Coil as a Magnetic
Dipole (5)
- 29: Additional Problems (16)
- 29: Guided Online Tutorials (6)
- Testbank (47)
- Symbolic Notation (7)
- Simulations (6)
- Conceptual Questions (8)
- Chapter 30: Induction and Inductance
- 30.1: What is Physics?
- 30.2: Two Experiments
- 30.3: Faraday's Law of Induction
- 30.4: Lenz's Law (20)
- 30.5: Induction and Energy Transfers
(8)
- 30.6: Induced Electric Fields (4)
- 30.7: Inductors and Inductance (2)
- 30.8: Self-Induction (4)
- 30.9: RL Circuits (8)
- 30.10: Energy Stored in a Magnetic Field
(5)
- 30.11: Energy Density of a Magnetic Field
(5)
- 30.12: Mutual Induction (5)
- 30: Additional Problems (18)
- 30: Guided Online Tutorials (6)
- Testbank (85)
- Symbolic Notation (4)
- Simulations (2)
- Conceptual Questions (9)
 (6)
(6)