INTRODUCTION
Because light can travel about seven and one—half times around the earth in one second, measurements of the speed of light have not always been easy.
The most elegant methods for speed of light measurements generally involve the use of a well collimated beam of light. Collimated light consists of parallel rays which do not decrease intensity with distance. Rays from conventional sources never originate from a single point and are difficult to collimate. On the other hand, a laser emits a beam that is already fairly well collimated and can be collimated even further using very simple optics. Therefore, a laser is the preferred choice for the light source in a speed of light measurement.
Michelson and Fizeau pulsed their light beams using choppers or rotating mirrors. These are cumbersome to set up; in addition, electronically driven external modulators, or Pockel cells, are often used, but they are very expensive. Instead we will use a modulated laser: a laser in which the light itself is modulated as it is created. Modulation is the adding of information to a carrier. Laser light can be amplitude modulated by varying its brightness.
In this experiment the time is measured for a pulse of light to travel down the hall and back. A modulated laser is used to generate the light pulses, and the delay is measured with a fast scope. This permits a direct determination of the speed of light.
Two connectors, located on the rear end plate of the laser, permit a source signal to drive the laser. A miniature phone jack may be used for audio signals with 100 mV peak-to-peak signal level and 60K impedance. A BNC connector is available for video signals with a one volt peak-to-peak signal level and 8K impedance. The signal source may be a crystal microphone, signal generator, television camera, tape recorder, etc. The modulation band width ranges form 50 Hz to 1 MHz.
Theory
The speed of electromagnetic waves is predicted from Maxwell's equations to be
for all types of electromagnetic radiation (light, radio waves, etc) and in any frame of observation. This is one of the most amazing constants of nature. c also represents the maximum velocity to which any object can be accelerated from rest.
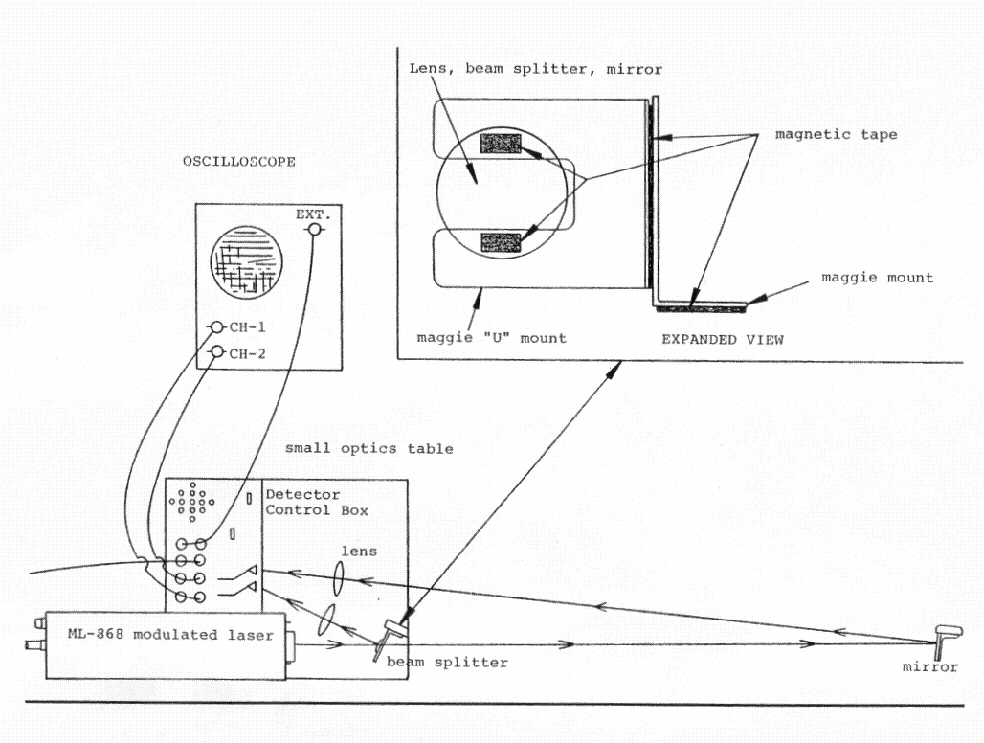
SPEED OF LIGHT MEASUREMENT
Equipment
What is the expected time delay for two pulses in the above experiment? What does this mean about how fast the oscilloscope needs to be able to take data?
Speed of light measurement setup is something like the diagram below. If you need things to make this happen, and you do not know where to find them, figure it out or ask.
NOTES: